Internet access in Russia is heavily censored. Ahead of the invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, this censorship has further increased. But how reliable is the censorship and how is the censorship technically implemented?
Extent
Censorship in Russia is not a new phenomenon. Efforts to restrict press freedom began as early as Putin’s first term in 2000-2004. Meanwhile, press freedom in Russia is no longer a given. In 2012, an extensive register of banned websites was published, which currently (as of 6.11.2022) contains 622,961 pages. An increase in blocked sites could already be observed ahead of the invasion of Ukraine:
The blocked websites cover a wide spectrum. For example, of the world’s most visited websites, the following sites were blocked in Russia as of early September 2022:
- facebook.com
- twitter.com
- instagram.com
- linkedin.com
- xhamster.com
- quora.com
On top of that, the websites netflix.com and weather.com have stopped service in Russia. Although the domains are not blocked, they are not available from Russia due to geoblocking:
Weather.com is not available in Russia.
While many international companies, such as Facebook or Google, have popular alternatives in Russia with vk.com and Yandex, the blocking of Instagram is particularly affecting Russian users. In 2021, the social network still reached 63.7% of users in Russia and, along with vk.com, was probably the most important social network in Russia. Since Instagram was blocked in March 2022, this share has likely declined noticeably despite the popularity of VPNs.
Especially Ukrainian websites, independent news and human rights organisations, which are particularly common in the sites that have been blocked since February, are affected by the blocking.
Technical implementation
Technically, Russia has opted for a decentralised approach in which the blocking has to be implemented by the Internet Service Providers (ISPs) (including VPN providers). A number of techniques are used for this:
DNS Block
The Domain Name System (DNS for short) is the system responsible for resolving domain names to IP addresses. Without the mapping of domains to IP addresses, the knowledge of the domain is no longer sufficient to reach a website. Therefore, DNS blocking is a common, but also easy to circumvent way of blocking websites. The DNS server either does not resolve a domain or deliberately resolves it incorrectly. This can be used to direct the user to a page that displays a blocking notification.

A DNS block can be bypassed via an alternative DNS server.
This technique can be circumvented by using an alternative DNS server (e.g. Google’s DNS 8.8.8.8 or Cloudflares 1.1.1.1).
MITM
A technique that is mainly used for unencrypted HTTP connections is a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM attack for short). A MITM attack exploits the fact that the data traffic is routed via a server of the ISP. The server controlled by the attacker (here the ISP) does not forward the request to the target server, but responds itself. Requests to a blocked website then never reach the target server, but are then answered with a blocking notification.

In an MITM attack, the attacker controls a node between the client and the server.
This procedure was also observed with TLS-encrypted HTTPS connections. Here, however, the browser detects the intrusion and displays a warning.
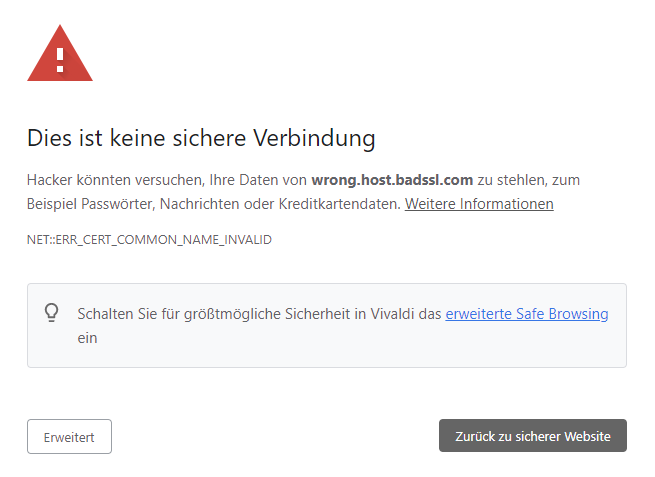
A warning is displayed in the event of a MITM attack on a TLS-encrypted connection.
Caution! This warning can be suppressed if the user trusts a CA to which Russian authorities have access (e.g. Russian Trusted Root CA of The Ministry of Digital Development and Communications).
Connection interruption
Instead of responding with a blocking notification, the connection can also simply be interrupted. At the Transmission Control Protocol level, this means that the ISP (similar to the MITM attack) does not pass on a connecting establishment to the target server, but resets the connection with an RST TCP packet.

The connection is interrupted by the ISP.
Alternatively, the ISP can either confirm the connection setup with a ACK SYN TCP packet (still without ever having forwarded the request to the destination server) or leave it completely unanswered. In both cases, the user’s client does not notice the interruption and waits for a response from the server until it terminates the connection itself with a timeout.

The client does not receive any feedback about the connection status.
Throttling
The previous options mean that the blocked pages are no longer accessible. In some cases, access to a page is only throttled. This means that the page is still accessible, but responds very slowly.
This method was observed in March 2021 during a failed test.
Deep Packet Inspection
While the implementation of internet blocking is required to be implemented by the ISPs, internet surveillance in Russia is implemented differently. Since 2015, all ISPs have been obliged to install a black box provided by the domestic intelligence service FSB in their network. These SORM-3 boxes are capable, among other things, of analysing data traffic by means of deep packet inspection and intercepting communication via mail or ICQ. These surveillance capabilities are used, for example, to identify government critics and peace activists.
Currently, a further intensification of surveillance efforts can be observed. In 2022, the penalties for ISPs which do not comply with the requirement to provide SORM-3 have been significantly increased.
Links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20221001211728/https://www.statista.com/statistics/867549/top-active-social-media-platforms-in-russia/ (As of 1.10.2022)
- https://web.archive.org/web/20221106193834/https://reestr.rublacklist.net/ru/statistics/ (As of 6.11.2022)
- https://www.reporter-ohne-grenzen.de/russland/ueberblick-russland
- https://www.similarweb.com/de/top-websites/
- https://www.stern.de/gesellschaft/traenenreicher-abschied-von-instagram-in-russland---er-wird-folgen-haben-31700056.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_Control_Protocol#Connection_establishment
- https://www.heise.de/news/Russland-Twitter-Drosselung-trifft-nicht-nur-t-co-sondern-t-co-5078788.html
- https://www.forbes.ru/tekhnologii/468229-mincifry-predlozilo-ne-vydavat-licenzii-na-uslugi-svazi-bez-ustanovki-sorm
